Bringing a new puppy home is a decision filled with excitement and joy. Often, we choose a breed based on its looks, personality, or size. However, beneath that adorable exterior lies a complex genetic blueprint that can predispose them to certain health conditions. Understanding puppy genetic diseases is not about fostering fear, but about empowering prospective owners with knowledge. This awareness is the first step toward responsible pet ownership, allowing you to choose an ethical breeder, recognize early warning signs, and provide a lifetime of proactive care.
This comprehensive guide will explore the common hereditary health challenges faced by popular dog breeds. We’ll demystify the science behind these conditions, provide a breed-by-breed breakdown, and, most importantly, outline the crucial questions to ask a breeder to ensure you’re welcoming the healthiest puppy possible. Your journey to informed ownership starts here.
Why Are Purebred Dogs Prone to Genetic Diseases? 🔍
The prevalence of certain puppy genetic diseases in purebred dogs is largely a result of selective breeding. While breeding for specific traits like a compact size, a flat face, or a herding instinct has given us the diverse breeds we love, it has also inadvertently concentrated harmful genetic mutations.
- The Founder Effect: Many breeds were established from a small number of “founder” dogs. If those founders carried a recessive gene for a disease, it became widespread in the entire gene pool.
- Popular Sire Effect: When a single male dog is extensively bred due to desirable show traits, he can pass on any hidden genetic disorders to a large proportion of the breed.
- Breed Standards: Unfortunately, some breed standards directly encourage physical traits that can cause health problems, such as extremely short noses (Brachycephaly) or sloping hips.
Key Genetic Health Screening Tests for Breeders 🩺
A responsible breeder doesn’t just breed two dogs; they breed two sets of health test results. Here are the most common screening tests:
- OFA (Orthopedic Foundation for Animals): Evaluations for hip and elbow dysplasia, thyroid disease, and heart conditions. Results are publicly registered.
- CERF (Canine Eye Registry Foundation): Annual eye exams by a veterinary ophthalmologist to screen for hereditary eye diseases.
- Genetic DNA Tests: Specific blood or cheek swab tests that can identify carriers of mutations for diseases like Degenerative Myelopathy (DM) or Exercise-Induced Collapse (EIC).
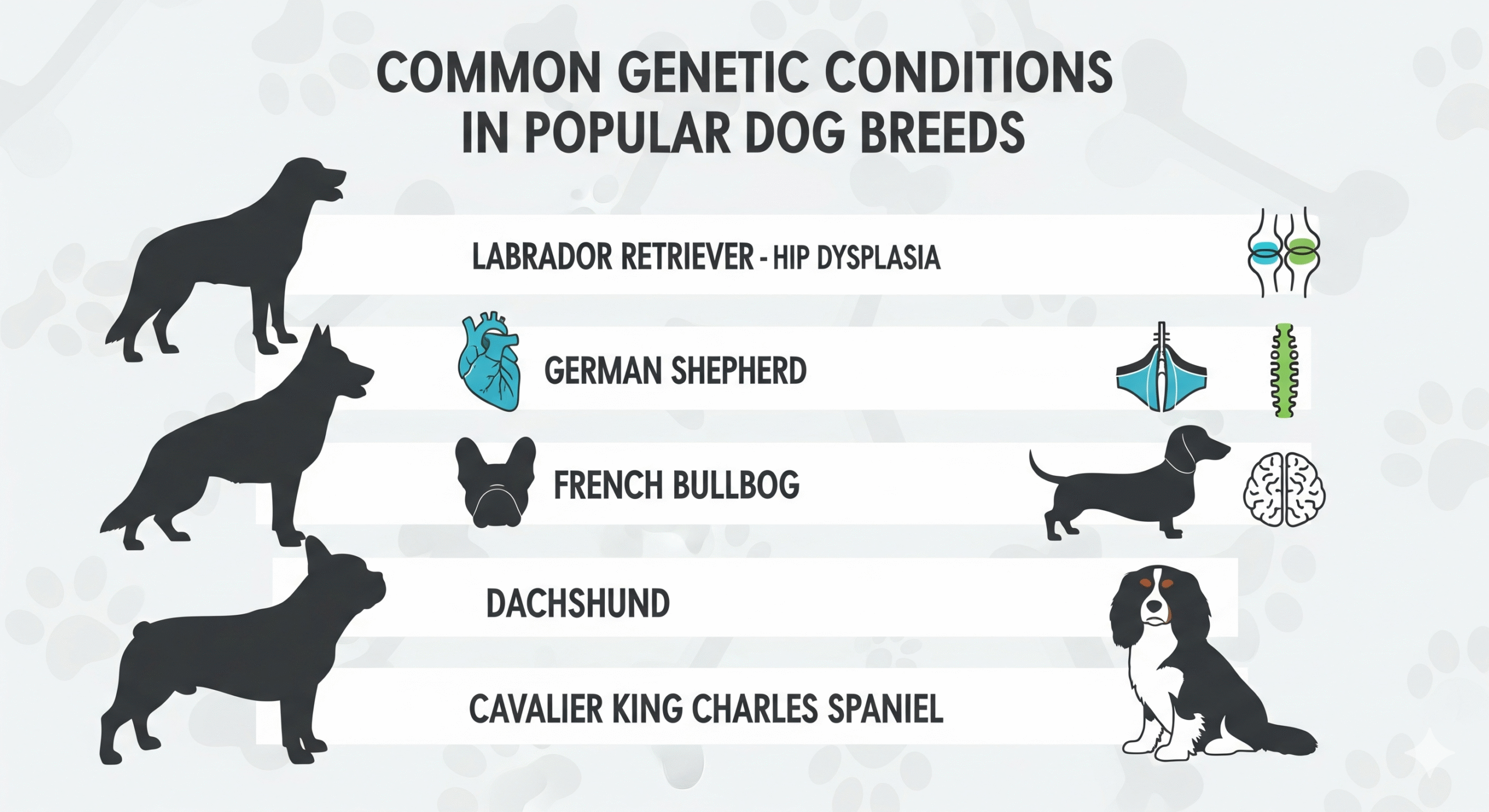
A Breed-by-Breed Guide to Common Genetic Conditions 📋
This list covers some of the most popular breeds and their associated health concerns. It is not exhaustive but highlights critical issues to be aware of.
1. Labrador Retriever 🦮
- Hip and Elbow Dysplasia: Malformation of the joints leading to arthritis and pain.
- Exercise-Induced Collapse (EIC): A neuromuscular disorder causing weakness and collapse after intense exercise.
- Centronuclear Myopathy: A hereditary muscle disorder causing weakness and awkward gait.
- Breeder Check: Ask for OFA/PennHIP scores for hips/elbows and DNA test results for EIC.
2. German Shepherd 🐺
- Hip and Elbow Dysplasia: Extremely prevalent in the breed.
- Degenerative Myelopathy (DM): A progressive and fatal disease of the spinal cord, similar to ALS in humans.
- Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI): The pancreas fails to produce enough digestive enzymes, leading to malnutrition and weight loss.
- Breeder Check: OFA scores are essential. DNA testing for the DM gene is crucial (a carrier is okay, but two carriers should not be bred).
3. Golden Retriever 🌟
- Cancer: Sadly, a leading cause of death, including hemangiosarcoma and lymphoma.
- Hip and Elbow Dysplasia: Common orthopedic issues.
- Heart Conditions: Particularly subvalvular aortic stenosis (SAS).
- Breeder Check: OFA scores for hips, elbows, and heart. Review the health history of the parents and grandparents.
4. French Bulldog, Pug, Boston Terrier (Brachycephalic Breeds) 😤
- Brachycephalic Obstructive Airway Syndrome (BOAS): The single biggest concern. Includes narrowed nostrils, elongated soft palate, and hypoplastic trachea, causing severe breathing difficulties.
- Heat Intolerance: Inability to regulate temperature effectively due to compromised breathing.
- Spinal Disorders: Like hemivertebrae, which can lead to pain and paralysis.
- Breeder Check: Prioritize breeders who prioritize health over extreme looks. Parents should have wide nostrils and should be able to breathe quietly after mild exercise.
5. Dachshund 🌭
- Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD): The long back and short legs make them extremely prone to slipped discs, which can cause pain, nerve damage, and paralysis.
- Breeder Check: While IVDD is a structural risk, breeders should still provide OFA scores and breed for longer legs and shorter backs to mitigate risk.
6. Cavalier King Charles Spaniel ❤️
- Mitral Valve Disease (MVD): A devastating heart disease where nearly all Cavaliers will develop a heart murmur by age 10, with many affected much earlier.
- Syringomyelia: A severe condition where the brain is too large for the skull, causing fluid-filled cavities in the spinal cord. Symptoms include neck pain and phantom scratching.
- Breeder Check: Ask for proof of annual heart exams (echocardiograms) from a cardiologist for both parents and their MVD breeding age guidelines. Parents should be MRI-scanned for Syringomyelia.
7. Boxer 🥊
- Boxer Cardiomyopathy (Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy): A serious heart condition that can cause sudden death.
- Cancer: Including mast cell tumors and brain tumors.
- Hip Dysplasia.
- Breeder Check: Heart screening via Holter monitor and echocardiogram is non-negotiable. OFA hip scores should be available.
What You Can Do: Questions for Your Breeder & Beyond 🤔**
As a buyer, you have the power to support ethical breeding practices.
Questions to Ask EVERY Breeder:
- “What genetic health screenings have both parents had? Can I see the official OFA/pennhip/eye exam results?”
- “Are you aware of any genetic diseases in this puppy’s bloodline?”
- “What is your health guarantee?”
- “Do you participate in any breed-specific health clinics or initiatives?”
Proactive Steps for Owners:
- Pet Insurance: Enroll your puppy early before any conditions are diagnosed.
- Know the Signs: Research the early symptoms of your breed’s common conditions.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight exacerbates almost every orthopedic condition.
- Consider Genetic Testing: Services like Embark can screen your adult dog for hundreds of genetic variants.
Conclusion: Knowledge is the Best Prevention</H2>
Understanding puppy genetic diseases is a fundamental part of choosing and caring for a purebred dog. It allows you to move beyond aesthetics and make a decision rooted in the long-term wellbeing of your future companion. By choosing a breeder who prioritizes health testing above all else, you are not just getting a puppy—you are investing in a healthier, happier future and supporting the ethical future of the breed you love.
🧪 Call to Action (CTA): What breed are you considering? Share your questions about their health below! For a printable checklist of questions to ask your breeder, subscribe to our newsletter.
“Annual vet check-ups are crucial for every dog, but for some breeds, standard care isn’t enough. Certain breeds require tailored preventative screening based on their known genetic risks. This means going beyond vaccines and heartworm tests to include specific checks for hips, eyes, or heart function. For example, owners of breeds prone to cardiac issues should discuss annual echocardiograms (heart ultrasounds) with their veterinarian. This is especially critical for breeds like the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel, where early detection is paramount. To understand the specific screening schedule and what to ask your vet, please read our dedicated article on Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Heart Health.”